VGG
5 July 2021
Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition (CVPR, 2014)
https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556
- 층을 깊게 쌓는 deep neural network의 시작
- 크기가 작은 필터 (= 적은 파라미터 수)를 가지고도 높은 정확도를 보임
configurations
- Architectures
- Convolution: layer depth의 영향을 확인하기 위해 kernel size는 3*3 (최소한)으로 고정
- Pooling: 2*2, stride 2 max-pool layers for 5 convolution layers
- stack of convolutional layers + FC layers + softmax layer
- Activation: ReLU
-
Configurations
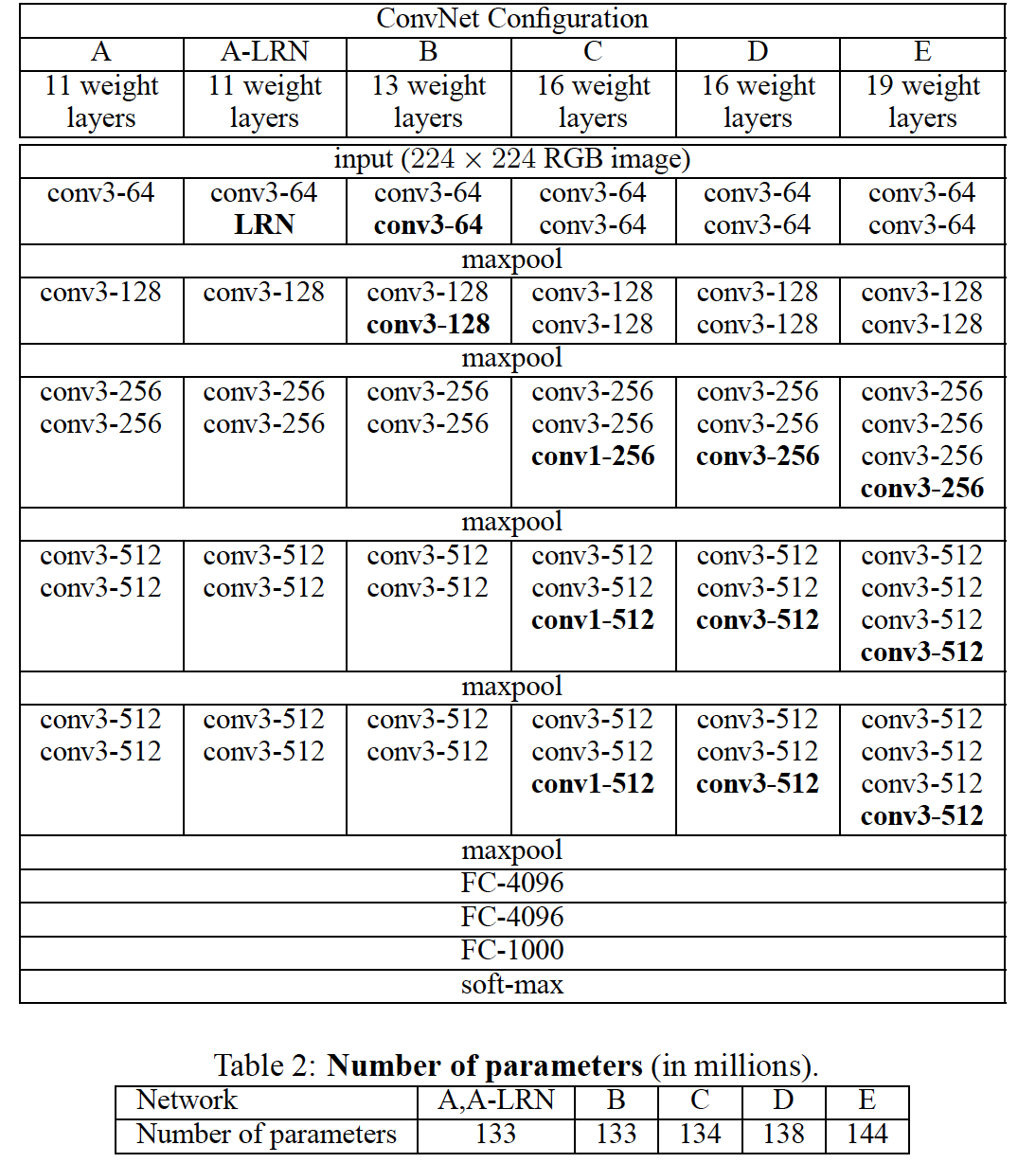
D: VGG16, E: VGG19
-
LRN: Local Response Normalization - 특히 높은 pixel 값을 normalize 해주는 것
increased memory consumption and computation time
- single 77 layer vs three 33 layers
- multiple activation layers → more discriminative decision function
- decreased number of parameters
-
1*1 layer
→ affect of increased non-linearity
→ dimensionality reduction (decreased channel size)
classification framework
batch size: 256, momentum: 0.9 (SGD)
regularization: weight decay, dropout 0.5 for FC layers
learning rate: 0.01, decreased by 0.1 if validation accracy stopped increasing
- required less epochs to converge due to
- implicit regularization by greater depth and smaller convolution
- pre-initialization of some layers using shallower network (VGG-A)
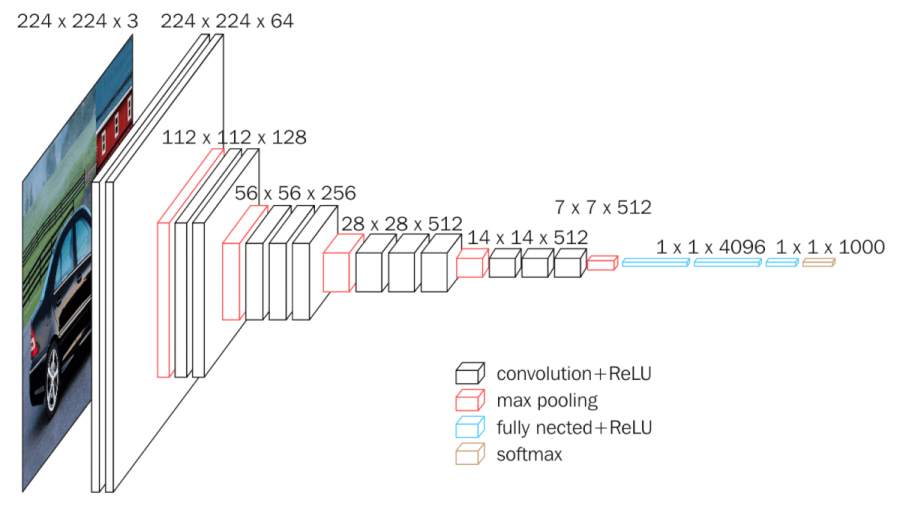
experiments
- dataset: ILSVRC-2012 (1000 classes, 1.3M training / 50K validation / 100K testing images)
- performance: top-1 error, top-5 error
- result
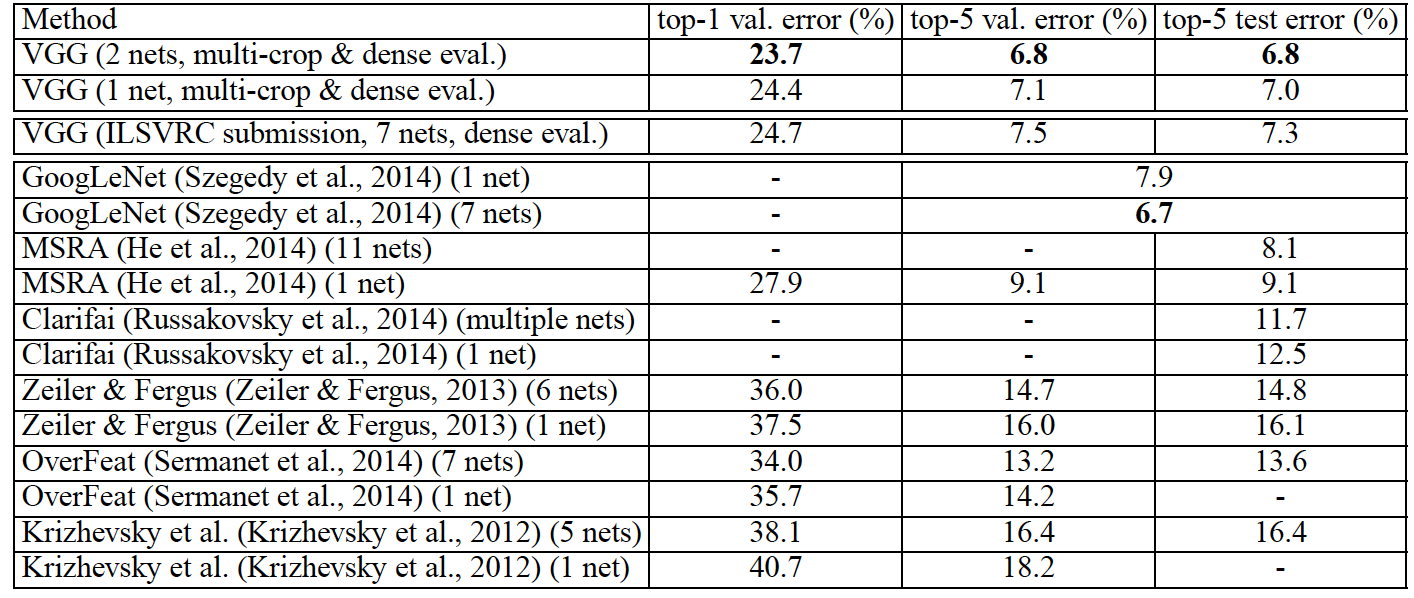
conclusion
- 간단한 구조로 좋은 성능을 구현
- 특징: 작은 kernel size로 반복되는 channel size를 여러개 쌓는 구조
- VGG16, VGG19를 주로 사용
- 매우 깊은 인공신경망 구조의 시작
