GCML
23 August 2021
Large Scale Video Representation Learning via Relational Graph Clustering (CVPR 2020)
Previous Work: CDML (Collaborative Deep Metric Learning for Video Understanding - KDD 2018)
- contributions
- limitations
- triplet loss → requires online negative mining →requires large batch size
- why? random initailization of the negatives
- randomly sampled negatives too far from the anchor
- triplet loss → requires online negative mining →requires large batch size
Motivation
- relational graph → learn representations that preserves relationships between videos
- node: video
- edge: similarity score between videos - binary / real numbers
- sparsely observed
- hierarchical clustering
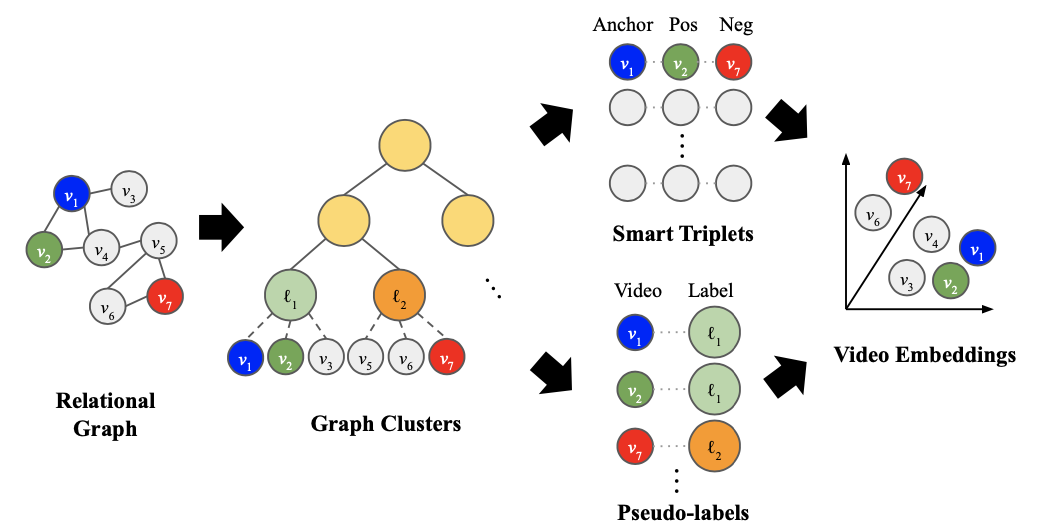
- approach 1) smart triplets
- generate training triplets
-
guarantee negatives with proper difficulty level
→ reduce training inefficiency of CDML
- approach 2) pseudo-classification
- classification model: cluster membership → target pseudo-label
- treat clusters as pseudo-labels
- semi-supervised learning: does not require any labeled data other than the relational graph
Methodology
- Graph Clustering
- relational graph → efficient data sampling
- any clustering algorithm is applicable: used affinity clustering
- hierarchical graph using minimum spanning tree → nearest neighbor clustering
- hierarchical: control difficulty of triplets to generate multiple levels
- affinity tree with 3 iterations
- intermediate nodes: clusters of the lower-level nodes
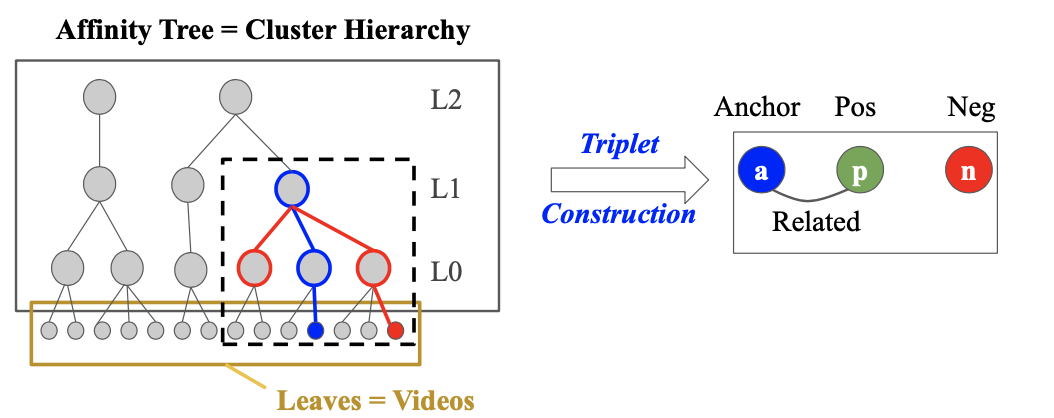
- [MODEL 1] Graph Clustering Metric Learning
- Smart Negative Sampling
- anchor: random video
- positive: chosen among neighbors of the anchor on the relational graph
- negative: chosen from the anchor’s sibling clusters (share the same parent)
- chosen at a desired level → can adjust difficulty level of the sampled negatives
- negatives not too far from the anchor: can be more informative for model training
- previous works: randomly sampled
- Training with Triplets
- triplet loss: relevant videos → closer, less related → further
-
dist(anchor, positive) < dist(anchor, negative)
\[min\sum_{i=1}^N[ ||f(x_i^a)-f(x_i^p)||^2 - ||f(x_i^a) - f(x_i^n)||^2 + \alpha]_+\] - online semi-hard negative mining
- re-sample negatives within each mini-batch: closest ones that are farther than positives from the anchors
- smart negatives would be consistently chosen
- Smart Negative Sampling
- [MODEL 2] Cluter Labels Classification
- training objective: classify which cluster each video belongs to
- classification model with sampled softmax
- sampled softmax: subset of sampled classes in each iteration
- benefit of classification
- no need to sample hard negatives
- removes dependency on batch size → more scalable
- training objective: classify which cluster each video belongs to
Experiments
Architecture
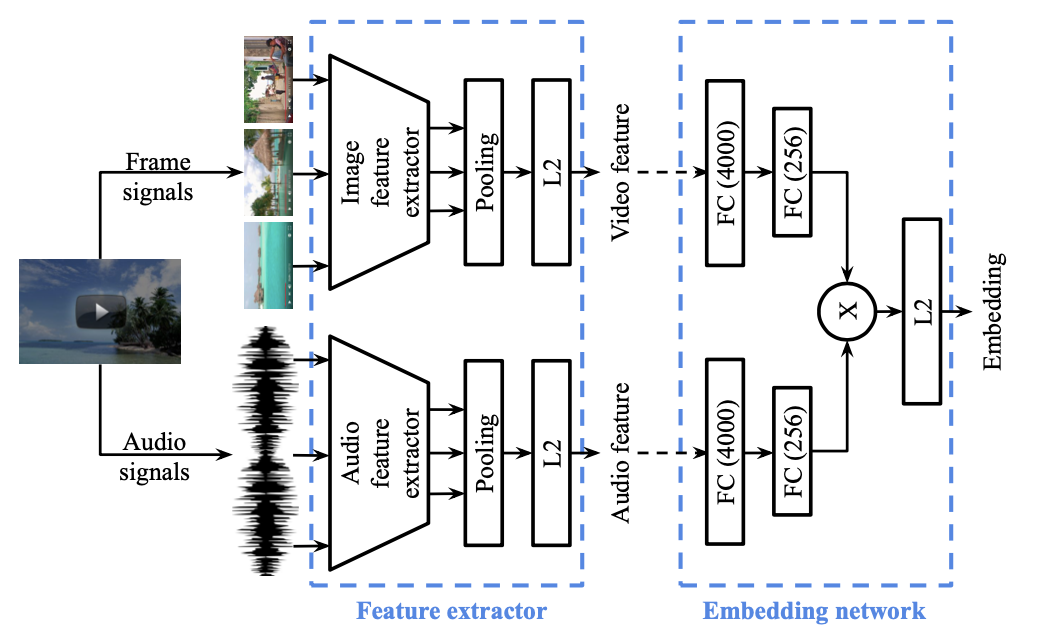
- Audio-visual Features
- features extracted with pre-trained models
- FPS: 1
- model: Inception-v2, pretrained on JFT dataset
- dimension reduction with PCA → 1500
- average pooling: frame level → video level
- audio: modified ResNet-50
- Embedding Network
- two FC layers
- two-tower model: each for visual and audio features
- aggregation: element-wise multiplication → L2 normaization
- loss: triplet loss or cross entropy loss
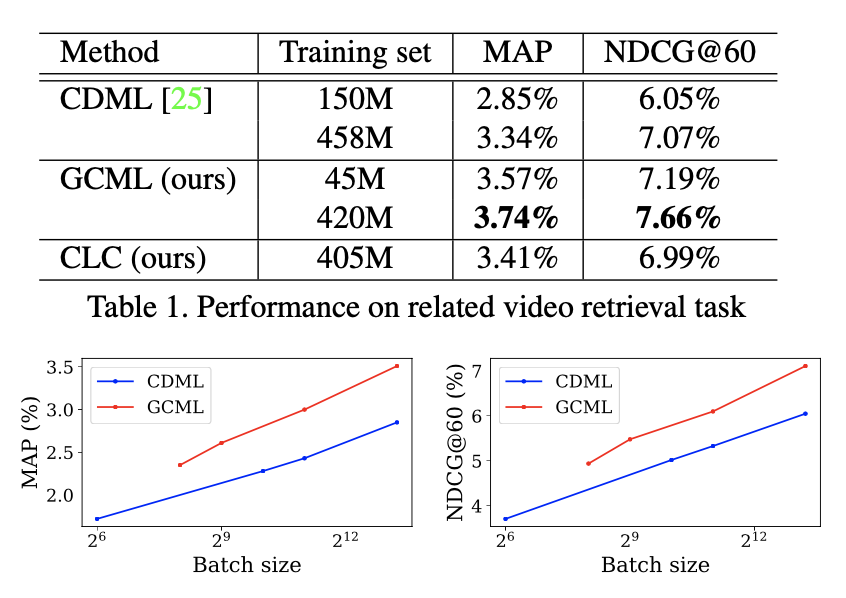
Task 1) Related Video Retrieval
- How?
- compute similarity score between two candidates (cosine similarity)
- candidates: based on relational graph
- Dataset
- YouTube-8M dataset (same as in CDML)
- Evalutation
- MAP
- NDCG@60
-
Results
Task 2) Video Annotation
- How?
- video embedding → FC layer → multi-label classifier
- Dataset
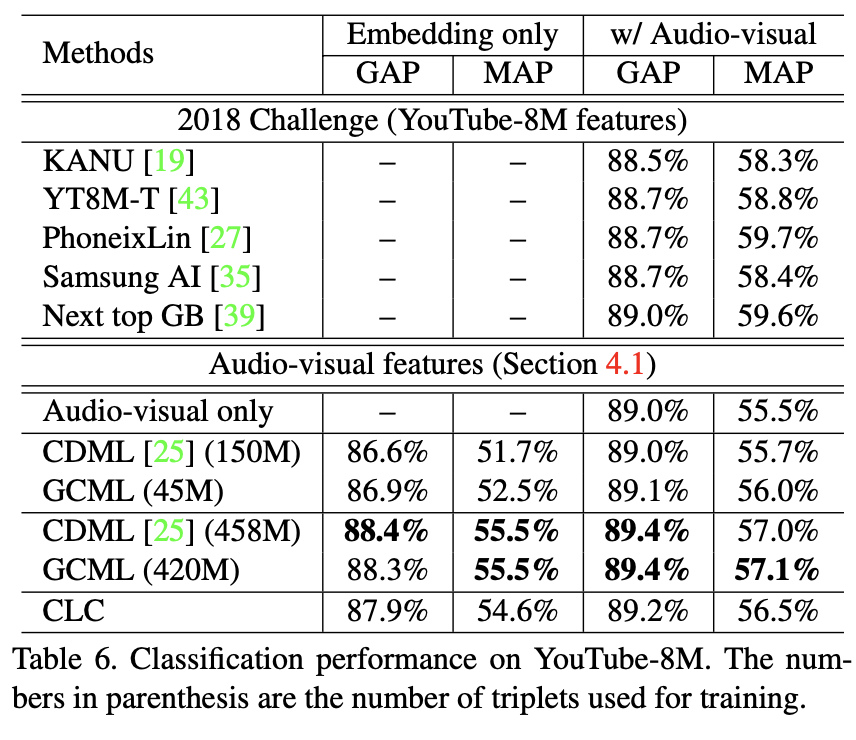
- YouTube-8M
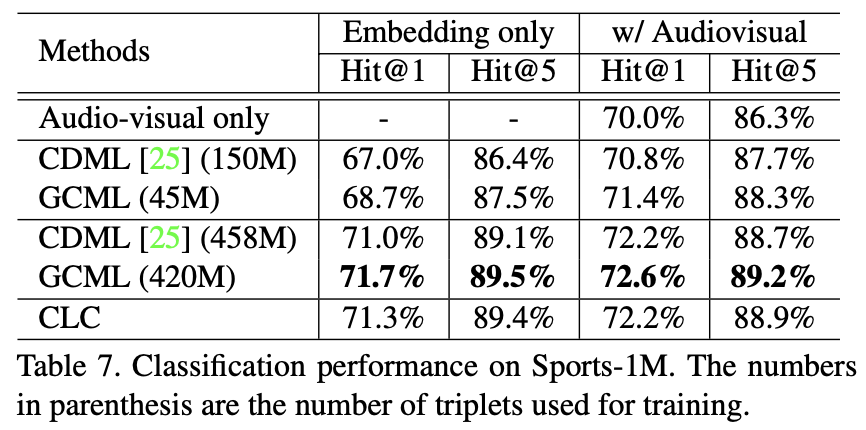
- Sports-1M
- Evaluation
- GAP, MAP
- Hit@1, Hit@5
-
Results