Fast R-CNN (ICCV 2015)
Main Idea
- R-CNN : multi-stage(proposal, detection, bbox) ⇒ Fast R-CNN : single-stage
- using multi-task learning
- 전체 이미지를 CNN에 넣음 (1 CNN on the entire image)
- 이전에는 Selective Search로 뽑아낸 모든 region proposal 후보들을 CNN 모델에 넣었음. (1 CNN per region)
- 2000 → 1
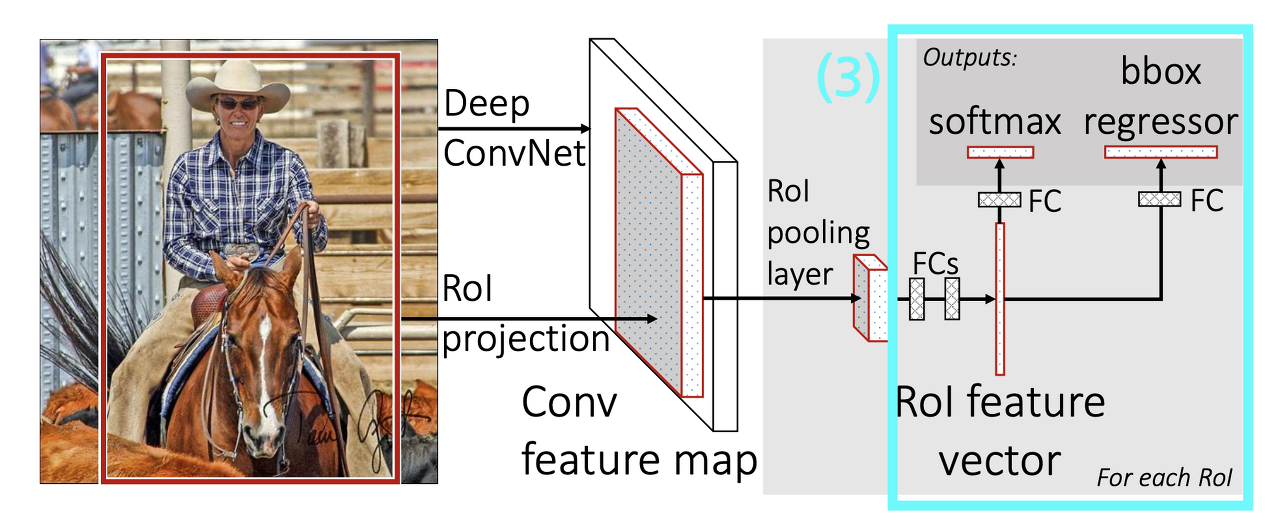
Fast R-CNN architecture
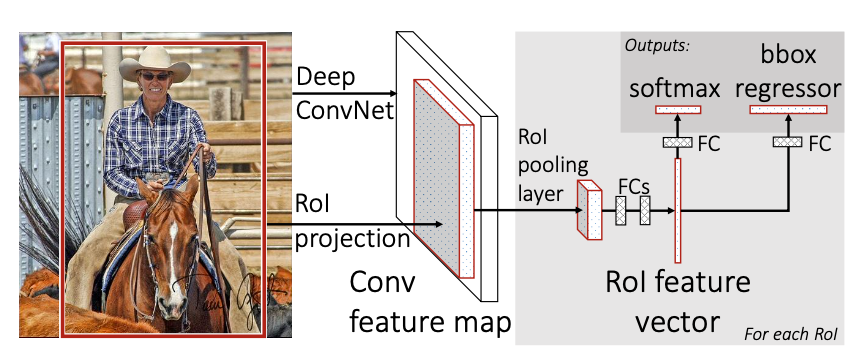
Process
- 전체 이미지를 CNN model에 통과시켜 Feature map 추출
- Selective Search를 통해 찾아낸 RoI들을 피쳐맵에 projection시키고, 각각의 RoI에 대해서 RoI pooling을 진행 ⇒ 고정된 크기의 feature vector 추출
- feature vector를 2개의 브랜치로 나눠 Fully Conneted layer에 통과
- [1번 브랜치] classification : softmax를 통과하여 해당 RoI가 어떤 오브젝트인지 분류 💥 output : softmax value → class
- [2번 브랜치] bbox regression : regression을 통해 selective search로 찾은 바운딩 박스 조정⇒ 올바른 bbox 좌표 예측 💥 output : bounding-box regression offsets
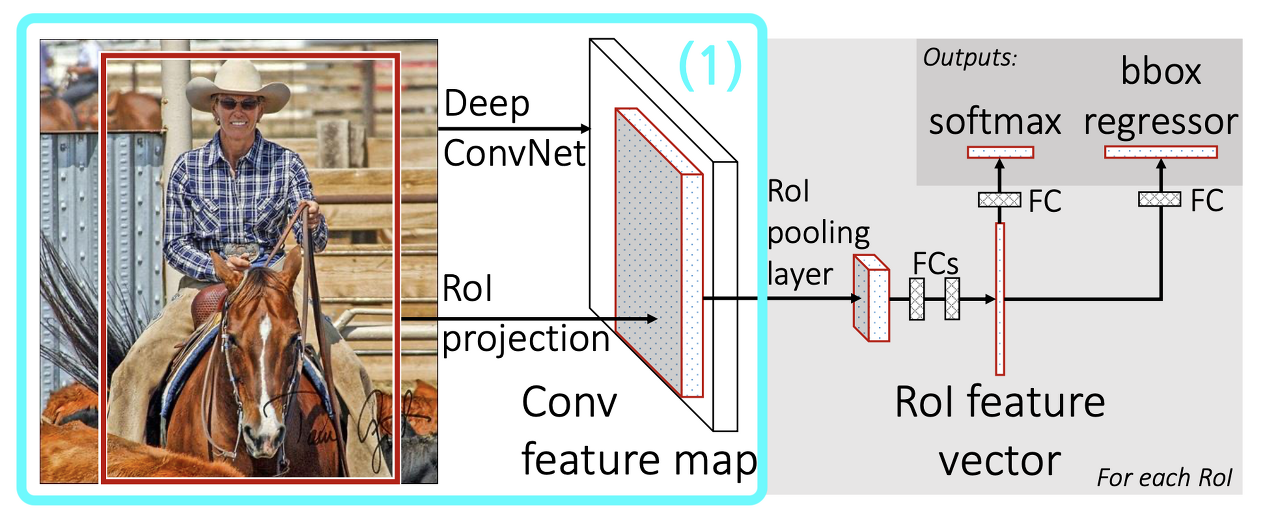
(1) Deep ConvNet & RoI Projection
https://nuggy875.tistory.com/33
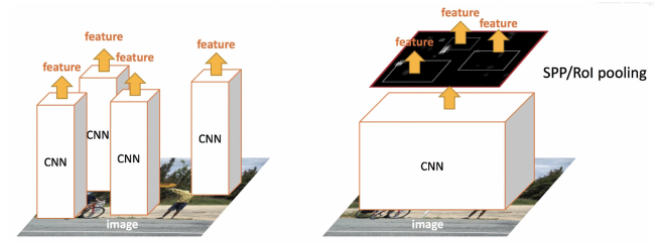
R-CNN 방식 vs. Fast R-CNN 방식
- R-CNN → Selective Search로 뽑아낸 Region Proposal 후보들을 모두 CNN에 넣어 시간이 오래 걸림
- Fast R-CNN → 1 CNN on the entire image
- Selective Search를 통해 Region Proposal은 함. R-CNN과 다르게 뽑아낸 영역을 그대로 가지고 있는 채로 전체 이미지를 CNN 모델에 넣음
-
🐳 CNN model의 ouput인 Feature Map에 RoI projection
🔍 RoI Projection : 인풋 사이즈와 피쳐맵 사이즈가 동일하다면 앞서 구한 RoI들의 좌표를 피쳐맵에 그대로 사용하면 되지만, 만약 다르다면 각 RoI들은 모델을 통과하여 줄어든 크기의 비율을 따져서 좌표를 변경시킴.
(2) RoI Pooling
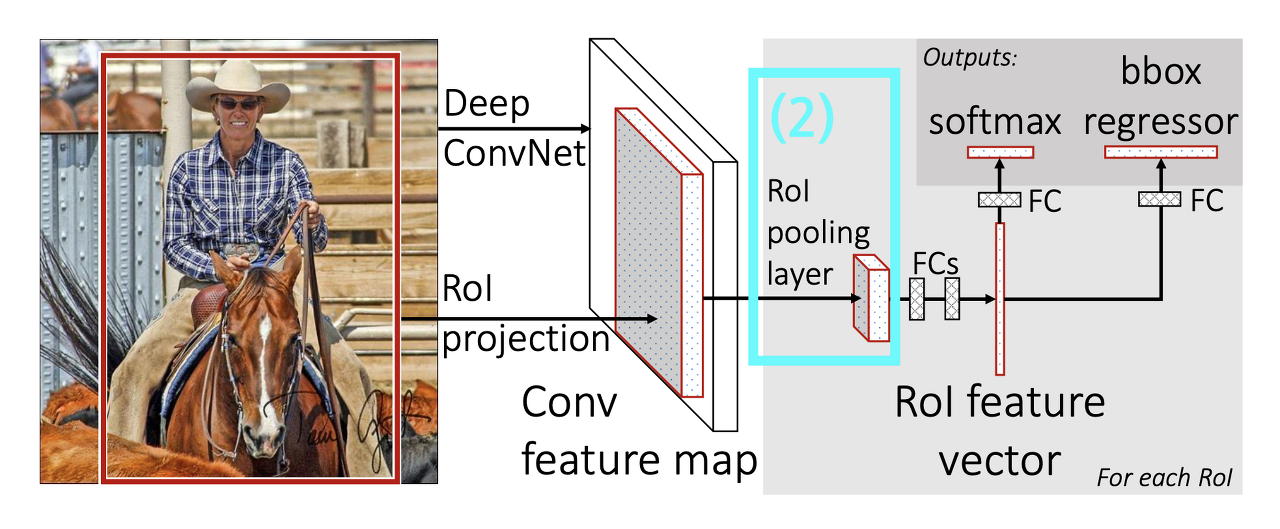
RoI들은 input 이미지에서 Selective Search를 통해 찾은 것을 feature map에 적용한 것이다.
- Selective Search로 통해 구한 RoI 영역을 각기 다른 크기를 가지고 있음
- FC : 고정된 크기의 인풋 필요
- ⛳️ GOAL: 다양한 크기의 RoI → 고정된 크기로 축소
- 이 RoI는 어느 시기의 피쳐맵을 사용?
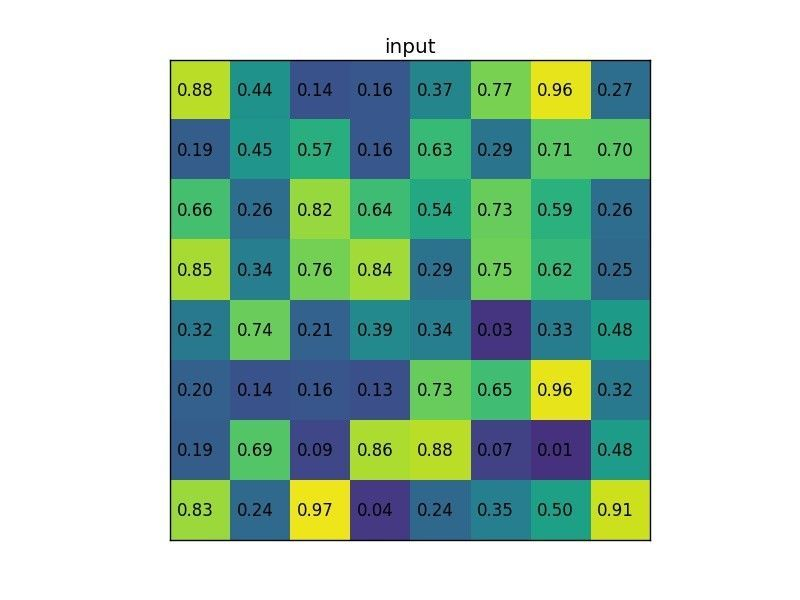
8x8 input feature map에서 Selective Search로 뽑은 7x5짜리 region proposal(아래)
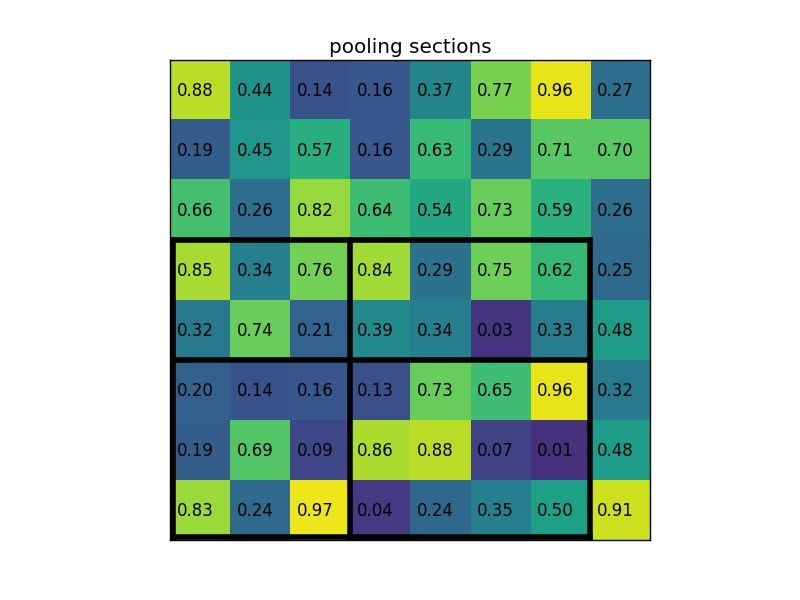
2x2로 만들기위해 Stride(7/2=3, 5/2=2)로 Pooling 구역을 정하고 Max Pooling → output : 2x2 (논문에서는 7x7 사용)

https://deepsense.ai/region-of-interest-pooling-explained/
- RoI에 다 적용 ⇒ 모두 다 같은 크기의 벡터 → FC layer
Classification & Bounding box Regression
**(FC layer)**
💥 input : 고정된 크기의 feature vector
💥 output1 : softmax value(classification)
💥 output2 : bounding-box regression offsets
=========
bbox regression => K + 1개 클래스에 대해서 각각 x, y, w, h 값을 **조정**하는 t_u를 리턴
==> 즉, 이 RoI가 사람일 경우 박스를 이렇게 조절해라, 고양이일 경우 이렇게 조절해라 라는 의미
Multi-task Loss
- $ L(p,u,t^u,v) = L_{cls}(p,u) + \lambda[u\ge1]L_{loc}(t^u,v) $
-
classification loss + bbox regression loss ⇒ multi-task loss $p=(p_0,…,p_K)$ : softmax를 통해 얻어낸
K+1(K-classes + None)개의 확률값$u$ : 해당 RoI의 G.T 클래스 값
[u≥1]은 G.T label이 Background (u=0)이면 Lloc term 날림.
🤷🏻? ⇒ Bounding Box를 치고자 하는 대상은 Background가 아닌 Object이기 때문이다.$t^u=(t_x^u,t_y^u, t_w^u,t_h^u)$ : bbox regression offset (예측한 bbox 좌표를 조정하는 값)
$v$ : ground truth bbox 조절 값
- $L_{cls}(p,u) = -\log p_u$
-
$L_{loc}(t^u,v) = \sum_{i\in{x,y,w,h}} smooth_{L_1}(t_i^u-v_i)$
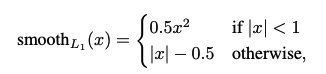
-
Experiments
- State-of-the-art mAP on VOC07, 2010, and 2012
- Fast training and testing compared to R-CNN, SPPnet
- Fine-tuning conv layers in VGG16 improves mAP
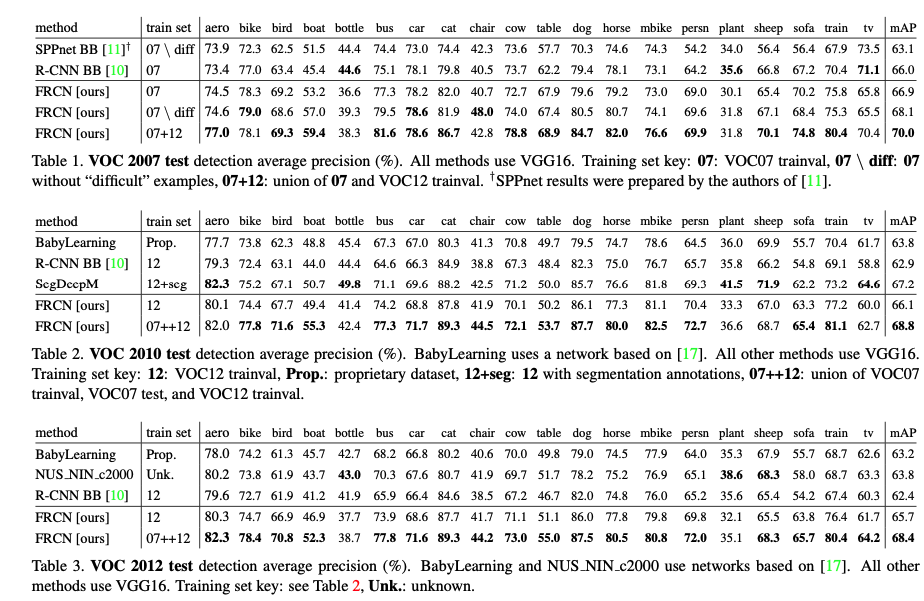
- Discussion : 왜 성능이 더 좋아졌는가? RoI 풀링의 효과인가 정말?
Conclusion
- 뛰어난 성능
- End-to-End Single Stage Training
- No disk storage is needed
- R-CNN → CNN에서 나온 피쳐맵을 디스크에 저장해두고 classification, bbox regression할 때 불러옴
